Headlines and events archive
Displaying 101 - 150 of 354
You may also find an archive of news published in the media which are related with the Instituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía - CSIC.
Pages
|
10/08/2021
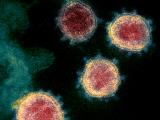
New technique to detect, without contact, viruses on surfaces Based on the use of hyperspectral images and data processing with advanced statistics and artificial intelligence, it has been successfully applied in two synthetic models of SARS-CoV-2. The research, which continues in humans, has been funded by the Carlos III Health Institute and has made it possible to patent a technique capable of simultaneously analyzing numerous samples without the need for contact or reagents |

|
02/08/2021
The Perseid meteor shower arrives The Perseids are produced by the impact in our atmosphere of fragments of the meteoroid cloud of Comet 109P / Swift-Tuttle, and are also recorded on the surface of the Moon. During the peak, around August 11, up to fifty perseids per hour can be observed in places away from light pollution |

|
29/07/2021
Small force, big effect: how planets can affect the Sun The Institute of Astrophysics of Andalusia (IAA-CSIC) is involved in developing a theory that supports the hypothesis that planets affect the Sun's magnetic activity. It shows how the small influence of the planets could set a rhythm in a system like the Sun that, if confirmed, would allow events such as solar storms to be predicted more accurately |

|
26/07/2021
The massive star that barely shone upon death The IAA-CSIC participates in two articles that disseminate the discovery of the shortest gamma ray burst (GRB) produced by the death of a massive star ever detected |

|
21/07/2021
The enigmatic assembly process of the Sombrero galaxy The Sombrero galaxy, a strange hybrid between a spiral and an elliptical galaxy, has been observed in detail to look for clues about its formation process. A large elliptical structure surrounding the galaxy, the product of a minor merger with another galaxy, has been characterised, but the origin of its shape remains unknown |

|
19/07/2021
The Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) pinpoints the central black hole of the galaxy Centaurus A The EHT collaboration, in which the IAA-CSIC participates, shows in unique detail the heart of Centaurus A, from which gigantic jets of matter emerge, giving it its characteristic appearance. |

|
15/07/2021
MeerKAT discovers a group of galaxies hidden in a well-studied region Su abundancia en hidrógeno neutro apunta a que se trata de un grupo de galaxias en proceso de formación |

|
30/06/2021
CARMENES instrument finds two new planetary systems formed by Earths and super-Earths The Institute of Astrophysics of Andalusia (IAA-CSIC) leads the detection of what, according to the data, is the most common type of planetary systems around dwarf stars, the most common in the Milky Way |

|
18/06/2021
CAIRT mission, with the participation of the IAA-CSIC, candidate for ESA's Earth Explorer 11 programme The mission will focus on processes combining atmospheric circulation, composition, space weather and regional climate change, and will provide critical observations not available with existing or planned satellites |

|
08/06/2021
IAA researchers publish the most detailed star catalogue of the Galactic Centre The GALACTICNUCLEUS project will make it possible to study the stellar population surrounding the supermassive black hole at the Galactic Centre in unprecedented detail. The work, led by the Institute of Astrophysics of Andalusia, offers the most extensive census of stars in the Galactic Core recorded to date |

|
24/05/2021
Juice mission prepares for its extreme environmental test JUICE, a European Space Agency (ESA) mission to be launched in September 2022, will study Jupiter and its moons to analyse the possibilities for the development of life around gas giant planets. The Institute de Astrophysics de Andalusia (IAA-CSIC) is participating in two of the mission's instruments, the GALA laser altimeter and the JANUS camera |

|
30/04/2021
Presentation of the project Hola Tierra The Institute of Astrophysics of Andalusia (IAA-CSIC) welcomes the presentation of the project of the musician Antonio Arias based on the poems of the astronaut Al Worden. The project, which has the participation of the Cervantes Institute and the IAA-CSIC, includes an album, a book and a documentary |

|
26/04/2021
A method to study distorted white dwarf stars is developed The IAA-CSIC is leading a study to determine the properties of stars that, either because of rapid rotation or because they are in a very compact double system subject to strong tidal forces, show a flattened shape |

|
16/04/2021
OPTICON-Radionet PILOT (ORP), the largest astronomy network in Europe, is born Two astronomy networks come together to form the largest collaborative terrestrial astronomy network in Europe |

|
12/04/2021
What ignites the helium halos of early galaxies remains a mystery A study looks at the galaxy IZw18, an analogue of the first galaxies that appeared in the universe, for the origin of the radiation that produces a helium halo around it |

|
30/03/2021
MAAT: new “eyes” for the OSIRIS instrument of the Gran Telescopio Canarias (GTC) MAAT, a visiting GTC instrument in the preliminary design phase, will bring the technique known as integral field spectroscopy to the OSIRIS instrument |

|
24/03/2021
Astronomers Image Magnetic Fields at the Edge of M87’s Black Hole The Event Horizon Telescope reaches a new milestone in astronomical observation by analyzing M87's supermassive black hole in polarized light |

|
10/03/2021
Observed for the first time a jet of gas as it emerges from the central star of a planetary nebula Thanks to MEGARA instrument of the Gran Telescopio Canarias, researchers from the Institute of Astrophysics of Andalusia (IAA-CSIC) have observed and analyzed the jet of NGC 2392, which points to the existence of a companion star |

|
02/03/2021
Researcher Mirjana Povic receives the Jocelyn Bell Burnell Award from the European Astronomical Society Researcher at the Ethiopian Institute of Space Science and Technology and a vinculated doctor to the Institute of Astrophysics of Andalusia, she investigates the formation and evolution of galaxies. She works in the development of science and education in Africa, with a special focus on the role of women, and has coordinated and participated in projects in Ethiopia, Uganda, Rwanda, Tanzania, South Africa, Kenya and Ghana |

|
23/02/2021
The Exoplanet Revolution Didier Queloz, 2019 Nobel Prize in Physics for the discovery of the first exoplanet around a star similar to the Sun, will give a seminar on the planetary systems found to date and their implications for our vision of the universe |

|
15/02/2021
The IAA Advanced School of Planetary Systems, open to the public Organized within the framework of the Severo Ochoa-IAA project, it addresses our knowledge of exoplanetary systems from a broad and updated context |

|
10/02/2021
ExoMars mission discovers new gas and tracks water loss on Mars The ExoMars-TGO orbiter, from the European Space Agency and Roscosmos, finds hydrogen chloride in the Martian atmosphere, produced by the release of salt embedded in the planet's surface. The ExoMars data also allow quantifying the loss of water on the red planet and establishing the mechanisms that contribute to the process |

|
04/02/2021
The largest radioastronomy observatory in the world, SKAO, is born Spain is among the participating countries in the SKA Observatory (SKAO), an intergovernmental organization that will open a new era in radioastronomy. The Minister of Science, Pedro Duque, has highlighted that it is a milestone that will revolutionize astronomy and other scientific and technological fields. Spanish participation in SKA is led by the Institute of Astrophysics of Andalusia (IAA-CSIC) |

|
03/02/2021
A "magnifying glass" look at one of the largest known centaurs Thanks to a stellar occultation, astronomers were able to observe and determine the characteristics of 2002 GZ32, a centaur with a diameter of almost 400 kilometers on its major axis. Known for more than forty years, we have little information about this group of icy objects orbiting the Sun between the orbits of Jupiter and Neptune |

|
19/01/2021
The IAA develops a study that shows a decrease in light pollution in Granada during confinement Although similar studies have been carried out in other countries, this is the only one that has obtained results thanks to the combination of observations from the satellite and from the ground |

|
14/01/2021
A study of the radio emission of Proxima Centauri, the closest planetary system, opens a new path for the study of exoplanets Researchers from the Institute of Astrophysics of Andalusia (IAA-CSIC) are leading an ambitious radio observation project that shows that extrasolar planets can be detected with radio telescopes |

|
11/12/2020
Triple planetary conjunction: an ideal opportunity to enjoy the night sky This December, due to the alignment of the Earth, Jupiter and Saturn, we will be able to see the giant planets of the Solar System very close in the sky. Many activities are being organized to enjoy the event |

|
10/12/2020
RoadMap: studying the ubiquitous yet poorly known Martian dust As part of the European Horizon 2020 program, the RoadMap project (Role and impact of dust and clouds in the Martian atmosphere) has just started |

|
03/12/2020
The Stingray nebula, the youngest known, is fading Observations with the Hubble Space Telescope show how this young nebula has lost its brightness and changed shape in just two decades |

|
30/11/2020
MHONGOOSE begins to study the weak atomic gas that surrounds galaxies, key in their evolution MHONGOOSE, a legacy project of the MeerKAT radiointerferometer, South African precursor to the Square Kilometer Array, produces its first results. They have been obtained in its preparatory phase, thus anticipating the window that will open to the understanding of the formation and evolution of galaxies |

|
23/11/2020
Ariel mission moves from blueprint to reality The mission, developed by the European Space Agency (ESA) and scheduled for launch in 2029, has moved from the study phase to the implementation phase, which involves selecting an industrial contractor to build the spacecraft. The Institute de Astrophysics of Andalusia (IAA-CSIC) participates in Ariel through two of its scientific working groups |

|
05/11/2020
Published the new J-PLUS catalog, with almost twenty million celestial objects The Institute of Astrophysics of Andalusia (IAA-CSIC) participates in the project, coordinated by the Center for the Study of Physics of the Cosmos of Aragon (CEFCA) |

|
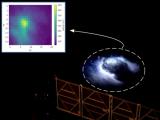
04/11/2020
Rapid radio bursts detected in our Galaxy The identification of a source producing very short duration radio bursts in our own galaxy, the Milky Way, is presented in three articles in the journal Nature. Studies suggest that a magnetar, a neutron star with a very intense magnetic field, would be behind this phenomenon |
|
23/10/2020
Confirmed the existence of a new electrical phenomenon in the atmosphere: blue flashes produced by cold electrical discharges Unlike lightning, these electrical discharges very efficiently activate certain chemical reactions that can produce nitrous oxide and ozone, gases that contribute to the greenhouse effect. The study, led by researchers from the Institute of Astrophysics of Andalusia (IAA-CSIC), has been possible thanks to data provided by the ASIM space mission of the European Space Agency (ESA) |

|
23/10/2020
The Galactic Center: a unique laboratory for the study of black holes Andrea Ghez, Nobel Prize in Physics 2020, will give an online conference on the center of the Milky Way next Thursday, October 29 |

|
23/09/2020
Wobbling Shadow of the M87* Black Hole Analysis of the Event Horizon Telescope observations from 2009-2017 reveals turbulent evolution of the M87* black hole image |
|
16/07/2020
The SO/PHI instrument, on board the Solar Orbiter mission, obtains the first autonomous magnetic map of the Sun The SO/PHI instrument, on board the Solar Orbiter mission, obtains the first autonomous magnetic map of the Sun |

|
16/07/2020
IAA researchers participate in GRANDMA, an international network for the study of gravitational wave sources IAA researchers participate in GRANDMA, an international network for the study of gravitational wave sources |

|
16/07/2020
First technical light of the JPCam panoramic camera at the Javalambre Astrophysical Observatory First technical light of the JPCam panoramic camera at the Javalambre Astrophysical Observatory |

|
25/06/2020
Two super-Earths found around the brightest red dwarf star in our solar neighborhood The Institute of Astrophysics of Andalusia (IAA-CSIC) participates in the discovery of a multiple planetary system around GJ887, a star located 10.7 light years away |

|
15/06/2020
Detection of the green line of oxygen in the atmosphere of Mars NOMAD instrument, aboard the ExoMars (ESA) mission in orbit around Mars, has detected this diurnal emission of atmospheric oxygen for the first time outside Earth. The green line provides information on the composition and dynamics of the atmosphere, and this detection has also allowed to resolve a controversy between atmospheric measurements on land and atomic calculations |

|
10/06/2020
Astronomers discover that novae, a type of explosions in double star systems, expand non-stop The Institute of Astrophysics of Andalusia (IAA-CSIC) participates in the study of the expansion of the shell of material ejected by various nova explosions. They find that, contrary to what was assumed, novae expand unrestrained until their end, when they end up dissipating in the interstellar medium |

|
04/06/2020
First detection in autumn of an elevated stratopause, a winter atmospheric phenomenon Researchers from the Institute of Astrophysics of Andalusia detect, in data files from 2009, an elevated stratopause in November, a phenomenon never seen outside the winter period |

|
22/05/2020
IAA cosmic dust laboratory reinvents itself to study the detection of coronavirus on surfaces The Institute of Astrophysics of Andalusia (IAA-CSIC) is involved in a project financed by the Carlos III Health Institute for the development of a prototype to analyze surfaces contaminated by SARS-CoV-2. The IAA will contribute with polarimetry studies to the project, which already combines image acquisition in the entire optical and sub-millimeter range and its analysis with artificial intelligence |

|
05/05/2020
The IAA studies the influence of state of alarm on light pollution levels The project, developed by the IAA-CSIC Sky Quality Office and with the support of the Granada City Council, will analyze how current environmental conditions have affected light pollution levels |

|
07/04/2020
The Event Horizon Telescope reveals unexpected structures in quasar 3C279 About a year ago, the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) collaboration released the first image of a black hole. They have now looked in detail at the high-speed jet of material emerging from a supermassive black hole |

|
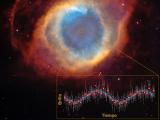
07/04/2020
The merger of two galaxies generates the juvenile version of a blazar, one of the most energetic objects known The first unequivocal detection of a jet of material at very high speed emerging from a galaxy in collision with another has been obtained. The jet emerges from the galaxy's central supermassive black hole and is seen head-on, a precursor structure to the formation of a blazar |
|
27/03/2020
A companion star: possible origin of the complex shapes of planetary nebulae Data from the TESS space telescope show variability in a sample of planetary nebulae, compatible with the presence of a companion star. This binarity could explain the complex morphologies of these objects, which result from the death of low and intermediate mass stars |

|
10/03/2020
The metamorphosis of a star in the final phases of its life ALMA radiotelescope captured a star in its evolution towards a planetary nebula |

|
09/03/2020
A thesis developed at the IAA is awarded the 2020 MERAC 2020 in new technologies (Instrumental) The optical engineer Concepción Cárdenas Vázquez has been awarded the MERAC Prize for the Best Doctoral Thesis in New Technologies (Instrumental) by the European Astronomical Society (EAS) |