Headlines and events archive
Displaying 201 - 250 of 354
You may also find an archive of news published in the media which are related with the Instituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía - CSIC.
Pages

|
03/07/2018
The atmosphere of Kelt-9b, the hottest known planet, is being dragged towards its star Similar to Jupiter, Kelt-9 is hotter than some stars. Thanks to the CARMENES instrument at Calar Alto Observatory, astronomers detected an extensive hydrogen envelope around Kelt-9b that escapes and is being captured by the star |

|
19/06/2018
Spain joins the SKA Organisation SKA is a worldwide scientific and technological project to build the largest radio telescope in the world. The Spanish participation has been led by the Institute of Astrophysics of Andalusia (IAA-CSIC) |

|
19/06/2018
The star distribution in clusters is established long before stars begin to shine The analysis of the Pipa nebula, a region of very early star formation, has confirmed that the density of the pre-stellar nuclei determines the geometry of the clusters |

|
14/06/2018
Astronomers See Distant Eruption as Black Hole Destroys Star First observation of the formation and expansion of a jet of material expelled by a supermassive black hole after destroying a star. The work, led by the University of Turku and the Institute of Astrophysics of Andalusia (IAA-CSIC), is published in the journal Science |

|
07/06/2018
The strange objects at the center of our galaxy: clouds of gas that behave like stars They could be stars blowted by the extreme gravity conditions around Sagittarius A *, the supermassive black hole at the galactic center. The results obtained on three of these objects after eleven years of observations with the Keck telescope (Hawaii) have been presented at the meeting of the American Astronomical Society (AAS) |

|
29/05/2018
The IAA, the only Spanish institution involved in JUICE (ESA), finishes the engineering phase of its contribution to the mission JUICE, a mission of the European Space Agency (ESA) that will be launched in 2022, will study Jupiter and its moons to analyze the possibilities of the development of life around the gas giant planets. The Institute of Astrophysics of Andalusia (IAA-CSIC) participates in two of the instruments of the mission, the GALA laser altimeter and the JANUS camera |

|
15/05/2018
Gigantic gas outflow generated by numerous supernova explosions detected in Arp 299-A galaxy Arp 299-A galaxy, which is in the process of merging with another galaxy (Arp299-B), is notable for its intense starbursts and its high rate of supernova production. New observations in radio have allowed to detect a filamentary structure that emanates from the nucleus, which is interpreted as a flow of gas at high speed |

|
25/04/2018
A Study Links Night Exposure to Blue Light with Breast and Prostate Cancer Researchers used images taken by astronauts to evaluate outdoor lighting in Madrid and Barcelona |

|
03/04/2018
SpaceX Launches ASIM mission (ESA), to study electric discharges in the upper atmosphere from the International Space Station The launch of the mission took place yesterday, April 2 at 22:30 from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida (USA). The Institute of Astrophysics of Andalusia (IAA-CSIC) participates in the analysis of mission data and through ground support with its own instruments |

|
26/02/2018
From Mars Express to Exomars: a complete review of the red planet While waiting for the first data from the ExoMars 2016 TGO mission (ESA), international experts on the red planet meet in Madrid to review some current challenges and to prepare for the arrival and scientific exploitation of ExoMars |

|
22/02/2018
POLAMI: a project to unravel the secrets of the supermassive black holes at the center of the galaxies Coordinated by the IAA, it brings together more than twenty researchers from five countries and is the first project of its kind: a long term study of the active galactic nuclei in polarized light |

|
12/02/2018
Solving the Dark Energy Mystery: A New Assignment for a 45-Year-Old Telescope Kitt Peak National Observatory Prepares for the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument |

|
30/01/2018
International Day of Women and Girls in Science The Institute of Astrophysics of Andalusia joins the celebration of the International Day of Women and Girls in Science, which seeks to make visible the scientific work of women and promote vocations in girls |

|
03/01/2018
Library of galaxy histories reconstructed from motions of stars The CALIFA survey allows to map the orbits of the stars of a sample of 300 galaxies, a fundamental information to know how they formed and evolved |

|
18/12/2017
CARMENES instrument finds its first exoplanet The planet HD 147379 b, with a mass slightly higher than Neptune, orbits a very close star |

|
22/11/2017
Artificially lit surfaces on Earth increase more than 2% per year Light pollution, produced mainly by excessive night lighting or incorrect lighting, is an energy waste that endangers human health and ecosystems. Between 2012 and 2016 artificial night lighting has increased by 9.1%, despite the use of more efficient lighting systems |

|
20/11/2017
MultiDark-Galaxies: a free access virtual universe An international team of astronomers has created a theoretical model that allows to recreate, in a broad and detailed way, the formation and evolution of the universe. The work provides an unprecedented test bench for new theories about the cosmos |

|
16/10/2017
The merging of two neutron stars allows the first simultaneous study in light and gravitational waves This is the fifth detection of gravitational waves, but the first in which the counterpart in electromagnetic waves is located and studied. Researchers at the Institute of Astrophysics of Andalusia (IAA-CSIC) take part in several international studies on the phenomenon |

|
11/10/2017
Haumea, the most peculiar of Pluto companions, has a ring around it The trans-neptunian belt contains four dwarf planets, among which Haumea stands out for its extremely elongated shape and rapid rotation. A stellar occultation makes it possible to establish main physical characteristics of heretofore this little known body – among which most surprising was presence of a ring |

|
04/10/2017
CARMENES instrument proves its ability to find Earth-like planets CARMENES, a visible and infrared spectrograph operating from the Calar Alto observatory (Almeria), is studying a sample of three hundred stars in search of Earth-like planets. The first results of the visible channel, derived from the study of seven planetary systems, show its perfect functioning |

|
27/09/2017
The Cherenkov Telescope Array (CTA), which will observe the most energetic universe from Chile and La Palma, publishes its scientific objectives With more than a hundred telescopes, the CTA is the largest project of study of the cosmos to high energies conceived. The project, which involves the Institute of Astrophysics of Andalusia (IAA-CSIC), is under construction and will start operating in 2024 |

|
14/09/2017
The unprecedented view of an exoplanet´s atmosphere Using the FORS2 instrument on ESO’s Very Large Telescope, astronomers have detected for the first time the presence of a metal oxide in the atmosphere of an exoplanet. This discovery opens the doors for detailed study of chemistry in exoplanetary atmospheres |

|
14/08/2017
The IAA will lead two of the five most advanced studies on supermassive black holes in 2018 The 66 antennas of the ALMA observatory join the Horizon of Events (EHT) telescope for the study of supermassive black holes. Five observation proposals have been approved for 2018, two of them coordinated by the Institute of Astrophysics of Andalusia (IAA-CSIC) |

|
21/07/2017
First light for MEGARA instrument on the Gran Telescopio Canarias The new 3D spectroscopy instrument, in which the IAA-CSIC participates, will make its first observations next Monday |

|
20/07/2017
Milky Way could have 100 billion brown dwarfs Brown dwarfs are objects intermediate in mass between stars and planets, with masses too low to sustain stable hydrogen fusion in their core |

|
04/07/2017
Improved Representation of Solar Variability in Climate Models New reference data set for model intercomparison studies published |

|
20/06/2017
Red Dots: The Live Search for Terrestrial Planets around Proxima Centauri Continues The Red Dots campaign will show how astronomers look for planets around Proxima Centauri, Barnard star and Ross 154 |

|
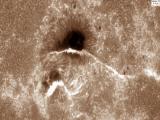
17/05/2017
Levels of light pollution soon to double if color of light is not taken into account Light pollution – produced by an excess of or incorrect nocturnal lighting – doesn’t just waste of energy, it also jeopardizes the health of human beings and ecosystems. Recent study shows importance of color of lighting, which most widely used sensors are blind to |
|
06/06/2017
IMaX, an instrument developed in Spain, analyses in detail the behavior of the Sun in full fledged activity IMaX, a magnetograph developed for the Sunrise mission, observed the Sun from a stratospheric balloon above the Arctic. A precursor to SoPHI, which will equip the Solar Orbiter mission, IMaX has made key breakthroughs to understand the magnetic field which determines the behavior of the Sun |

|
21/06/2017
Green light to PLATO, ESA's exoearth hunter With this mission Europe will lead the search for potentially habitable exoplanets. The Institute of Astrophysics of Andalusia participates in the project |
|
11/04/2017
Rewinding stellar evolution: The last 400,000 years of mass loss from a star The study of K4-37, a planetary nebula never studied in detail before, allows us to trace back the mass loss history of its last stages as a star. The study makes use of data from Calar Alto and San Pedro Martir (Mexico) observatories |

|
05/04/2017
OCTOCAM, a project lead by IAA astronomers, will be the next facility instrument of the Gemini observatory The twin Gemini telescopes, one of the most competitive observatories in the world, consists of two 8.1m telescopes in Hawaii and Chile. OCTOCAM will multiply the power of Gemini South by simultaneously observing in eight different bands |

|
21/03/2017
Rosetta mission describes surface change of comet in transit around the sun Comparative analysis of comet 67P’s surface before and after the perihelion (point on an orbit closest to the sun) reveals numerous changes in its orography, though not on a major scale. Paper published in Science magazine suggests important orographic features of comet 67P date back to previous, more active periods in its history |

|
14/03/2017
SN2015bh: the end of a star or an "impostor" supernova? Astronomers spot an intense explosion of a massive star, which, according to records, experienced frequent eruptions for at least 20 years. The analysis of the outburst does not allow to discern between a real supernova - an explosive event marks the end of a star - or a giant eruption implying a massive change in the star’s evolutionary course |
|
07/03/2017
Astronomers unveil with outstanding detail the first steps of nascent galaxies in the primeval universe An international team of astronomers have pushed large telescopes to their current limits to discover a population of tiny newborn galaxies, which shed new light into the first stages of galaxy formation. Although rare, these nascent objects reveal with unprecedented detail the extreme physical conditions that have existed in the first galaxies formed right after the Big Bang |

|
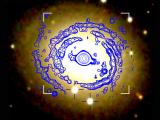
28/02/2017
P/2016 J1: an asteroid that split in two and whose fragments, years later, developed tails Asteroids, unlike comets, do not usually present tails, but there are some twenty exceptions to this rule. P/2016 J1 is a peculiar case, known as an “asteroid pair”, resulting from the fracture of a parent asteroid |
|
19/01/2017
Stellar formation is observed in a type of galaxy where, in theory, stars are no longer born CALIFA project allowed to detect, in three early-type galaxies, a very tenuous arms where stars are being formed. The data, obtained with Calar Alto Observatory 3.5m telescope, contradict the widespread belief that in old galaxies stars are no longer born |

|
29/12/2017
The Institute of Astrophysics of Andalusia launches the app "Let´s go to Mars!" "Let's go to Mars" is a scientific graphic adventure in which you must land-off in Mars, explore the surface of the planet, build a permanent base for the arrival of your colleagues, collect and analyze Martian samples, and face the many dangers that exist in the red planet |

|
30/11/2016
First data confirm that NOMAD will be able to put an end to the methane mystery on Mars NOMAD´s data confirm the perfect functioning of the instrument, co-developed by the Institute of Astrophysics of Andalusia (IAA-CSIC) |
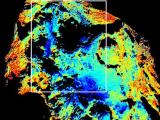
|
18/11/2016
Brightness variations on the surface of '67P / Churyumov' show the complexity of cometary activity Brightness variations on the surface of '67P / Churyumov' show the complexity of cometary activity |

|
14/11/2016
A startburst reveals the formation mechanism of massive stars A startburst reveals the formation mechanism of massive stars |

|
02/11/2016
Study confirms that novae, a type of explosive phenomenon in stars, are main source of lithium in the universe Large amounts of beryllium-7, an element that decays into lithium, have been found inside nova Sagittarii 2015 N.2 |

|
20/10/2016
ExoMars mission, in orbit around Mars The TGO satellite has successfully completed the ignition needed to be captured by Martian gravity |

|
29/09/2016
Rosetta's grand finale The spacecraft will perform tonight a controlled descent to the surface of the comet 67P, during which it will continue collecting data |
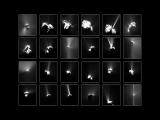
|
26/09/2016
Summer fireworks on Rosetta's comet Brief but powerful outbursts seen from Comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko during its most active period last year have been traced back to their origins on the surface |

|
22/09/2016
New breakthrough in methodology to estimate life span of stars Size of star nuclei determines amount of combustible available, and hence evolution and life span of a star |

|
15/09/2016
Mrk1018: the black hole that returns to the shadows Mrk1018 is a supermassive black hole located at the center of a distant galaxy that has changed its appearance twice in thirty years |

|
24/08/2016
Earthlike planet discovered orbiting around nearest star to Sun Located in the habitable zone, the planet orbits around its star in eleven days and has a mass of at least 1.3 times that of the Earth. Named Proxima B, it orbits around Proxima Centauri, a red dwarf located only four light years away from our own planet |

|
12/07/2016
University of Almería, Calar Alto Observatory and IAA will enhance astronomical knowledge Among the collaboration projects that will be launched, stand out the creation of an astronomical lecture room at the UAL, the incorporation of trainees at the Observatory and the creation of a summer course that approach its work to the whole society |
