
|
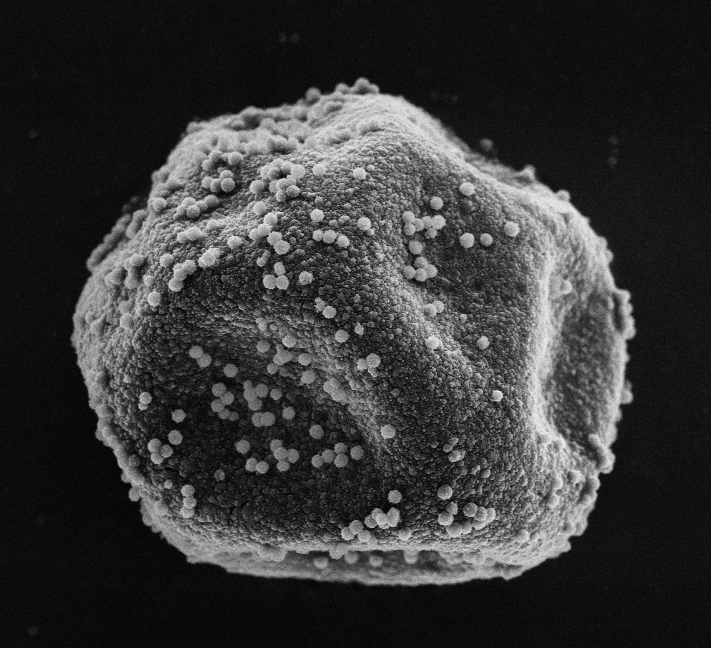
On the application of scattering matrix measurements to detection and identification of major types of airborne aerosol particles: Volcanic ash, desert dust and pollen Jun 2021 Atmospheric aerosols play key roles in climate and have important impacts on human activities and health. Hence, much effort is directed towards developing methods of improved detection and discrimina- tion of different types of aerosols. Among these, light scattering-based detection of aerosol offers several advantages including applications in both in situ and remote sensing devices. In this work, new scat- tering matrix measurements for two samples of airborne desert dust collected in Spain and China are reported. The average extrapolated scattering matrices of airborne desert dust and of volcanic ash at two wavelengths have been calculated and compared with the aim of finding criteria to distinguish these two types of aerosol. Additionally, the scattering matrix of cypress pollen has been measured and extrapo- lated to explore differences with mineral dust that can be exploited in atmospheric detection. Read more... |
|
ROADMAP - Role and impAct of Dust and clouds in the Martian AtmosPhere: from lab to space Nov 2020 ROADMAP is a H2020-SPACE-2020 new project CoDuLab is involved in. The goal of the project is to drastically enhance our knowledge of the Red Plant by focusing on the the prominent role of dust and clouds in its atmosphere. By combining light scattering experiments and observations, ROADMAP will study de composition of the Martian atmosphere, contribute to better understanding the physical processes in occurring in there and improve the modelling of dust and water cycles in it. Read more... |
|
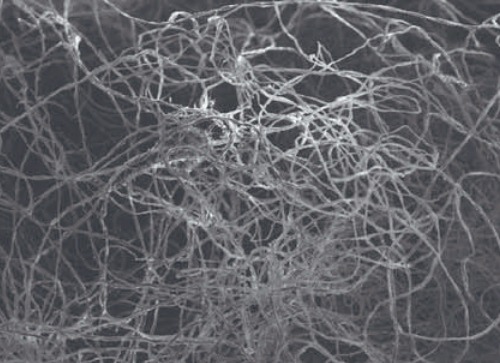
Experimental phase function and degree of linear polarization curves of millimeter-sized cosmic dust analogs Mar 2020 We present laboratory measurements of the phase functions and degree of linear polarization(DLP) curves of a selection of millimeter-sized cosmic dust analog particles. The set includes particles with similar sizes but diverse internal structure(compact and porous) and absorbing properties. The measured phase functions are found to be in all cases very different from those of micron-sized particles. They show a monotonic decrease with increasing phase angle from the back- to the side-scattering region, reaching a minimum at large phase angles before a steep increase of the forward peak.Read more... |
|
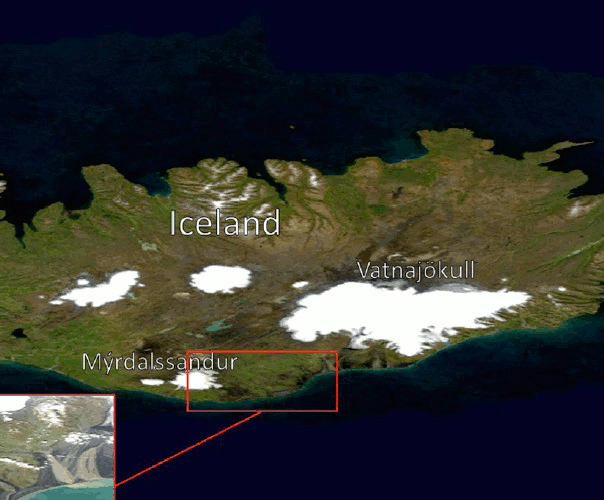
Light scattering from volcanic-sand particles in deposited and aerosol form Jul 2019 The light-scattering properties of volcanic sand collected in Iceland are studied here to characterize the sand particles and develop a reference for future remote-sensing observations. While such sand is common in Iceland, the smaller-size fraction can be readily transported by winds and found in the atmosphere at distant locations. The sand appears dark when deposited on a surface due to the high optical absorption of the material. Therefore, atmospheric regions containing such particles during a dust storm may absorb sunlight considerably, causing redistribution of solar energy. Here, we measure the angular scattered-light intensity and degree of linear polarization from the sand. Read more... |

|
Experimental phase function and degree of linear polarization of cometary dust analogues Jan 2019 We present experimental phase function and degree of linear polarization curves for seven samples of cometary dust analogues namely: ground pieces of Allende, DaG521, FRO95002, and FRO99040 meteorites, Mg-rich olivine and pyroxene, and a sample of organic tholins. The experimental curves have been obtained at the IAA Cosmic Dust Laboratory at a wavelength of 520 nm covering a phase angle range from 3◦ to 175◦. We also provide values of the backscattering enhancement for our cometary analogue samples. Read more... |